Metal stamping is a highly efficient manufacturing process used to shape metal sheets into intricate forms through various dies and presses. As an engineer or product designer, you may often face the decision of when to invest in tooling for metal stamping. Whether you are looking to produce a small batch of parts for a prototype, a moderate-sized production run, or a large-scale manufacturing operation, knowing when to invest in building a tool is critical to optimizing your costs, production efficiency, and overall success.
This comprehensive guide will help you assess the timing for tool investment based on your specific production needs, ranging from low-volume to high-volume manufacturing. By understanding the characteristics and considerations for each production volume, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.
Understanding Metal Stamping Tools
Before diving into the production volumes and related tooling considerations, it’s important to understand the different types of tools used in the metal stamping process:
- Single-Operation Dies: These are used for straightforward tasks such as cutting, punching, or blanking, and are generally used for simple part shapes.
- Progressive Dies: These tools perform multiple operations in a single pass, gradually forming the part as it moves through the die stages.
- Transfer Dies: Designed for complex parts, transfer dies move the part through different stations within the die, performing a sequence of operations on each pass.
The decision to invest in tooling will depend on the complexity of the part, production volume, and cost considerations. Below, we explore these aspects in relation to different production volumes to help guide your decision-making process.
Low-Volume Production: When Soft Tooling May Be a Better Option
Characteristics:
– Volume: Typically fewer than 10,000 parts.
– Tooling Costs: High relative to the production volume.
– Production Goals: Often for prototypes, test runs, or limited production runs.
Tooling Considerations:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Investing in a high-quality, durable tool for low-volume production may not be the most cost-effective decision. With fewer parts to produce, the tooling costs could significantly impact the overall project budget.
- Alternative Approaches:
– Soft Tooling: Consider using softer materials like zinc-based alloys or non-heat-treated steel. These materials are cost-effective for short runs and prototypes but have a shorter lifespan and reduced precision compared to hardened steel.
– Manual or Semi-Automatic Tools: For simple applications, manual or semi-automatic tools can provide a more affordable solution. These are suitable for low volumes where absolute precision is not critical.
– 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping: For prototyping, 3D printing offers a cost-effective way to create tooling for low-volume production. Although it’s not suitable for high-precision or high-stress applications, it’s an ideal method for design testing and small batches.
- Tooling Design: Focus on simplifying the tooling design to reduce costs, while still meeting the essential needs of your part.
Mid-Volume Production: Justifying the Investment in Durable Tooling
Characteristics:
– Volume: Between 10,000 and 100,000 parts.
– Tooling Costs: Substantial but spread across more parts.
– Production Goals: Often used for moderate-sized production runs, product testing, or market launches.
Tooling Considerations:
- Cost Efficiency: At this stage, investing in more durable and precise tooling becomes justifiable. The cost per part decreases, allowing you to recover the initial tooling investment over a larger number of units.
- Tooling Material:
– Hardened Steel Tools: Steel tools are ideal for mid-volume production. They provide better durability, precision, and the ability to handle higher production rates than soft tooling materials.
- Tooling Complexity:
– Progressive and Transfer Dies: Progressive and transfer dies are highly beneficial for mid-volume production as they improve efficiency by performing multiple operations in a single pass. This helps increase throughput and precision.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance becomes essential for ensuring that the tooling continues to operate efficiently. Robust tooling will withstand wear and tear, leading to consistent high-quality production.

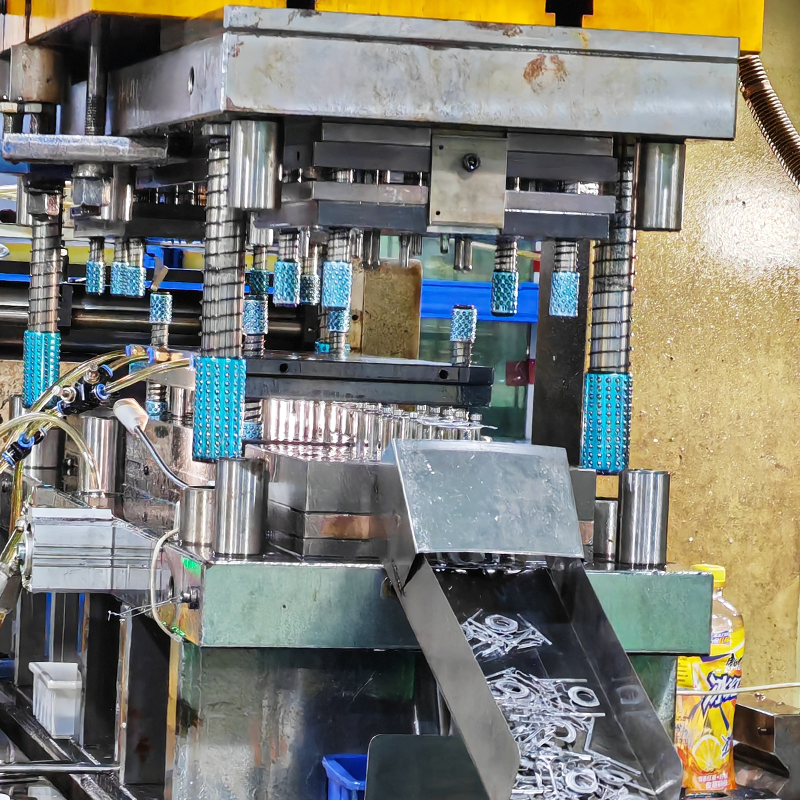
High-Volume Production: The Need for Advanced, Durable Tools
Characteristics:
– Volume: Typically exceeding 100,000 parts.
– Tooling Costs: High, but cost-per-part is low due to the large production scale.
– Production Goals: Large-scale manufacturing aimed at cost-efficiency and high precision.
Tooling Considerations:
- Investment Justification: Although the initial cost of tooling is high, it is justified by the low cost-per-part achieved in large-volume production. The focus is on maximizing production efficiency and minimizing part cost.
- Tooling Material:
– Hardened Steel Tools: Hardened steel tools are essential for high-volume production. They offer superior durability, precision, and longevity, which are critical for maintaining high production rates and consistent part quality.
- Tooling Complexity:
– Advanced Dies: For high-volume production, advanced dies are often required. These dies may include multiple stations or complex operations, designed to handle intricate parts with high throughput. Progressive and transfer dies are common in high-volume applications due to their ability to manage multiple operations in one pass.
- Production Efficiency and Automation:
– Automation: High-volume production often involves automated processes to enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure consistent part quality. Automation helps to further boost production speed and consistency.
- Maintenance and Quality Control: For large-scale production, continuous maintenance and robust quality control systems are crucial to avoid downtime and ensure all parts meet exact specifications.

Summary
When considering whether to invest in building a tool for metal stamping, the following factors should guide your decision:
- Production Volume:
– Low Volumes: Soft tooling or alternative methods may be more cost-effective for low-volume runs.
– Mid Volumes: Durable tooling becomes more justifiable, offering greater efficiency and precision.
– High Volumes: Advanced, high-durability tooling is essential for maximizing efficiency and maintaining consistent part quality.
- Cost Considerations: Compare the cost of tooling to the production volume and evaluate alternative manufacturing methods. At mid to high volumes, the cost-per-part decreases, making it easier to justify the tooling investment.
- Part Complexity: More complex parts may require investment in advanced tooling, especially at higher volumes, to ensure accurate and efficient production.
- Production Goals: Consider your overall production goals—whether it’s a prototype, limited production run, or large-scale manufacturing—and choose the tooling that best aligns with these objectives.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your production needs, timeline, and budget.
Why Choose Thesun Industry for Your Metal Stamping Needs?
At Thesun Industry, we specialize in providing high-quality, cost-effective solutions for all your metal stamping needs. With over two decades of experience, our team has the expertise to handle projects across a wide range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and consumer electronics.
Whether you need precision progressive die stamping, deep drawing, or complex metal forming, we are equipped with cutting-edge manufacturing technology and a skilled workforce to meet your production requirements. Our commitment to excellence ensures that we deliver parts that meet the highest standards of quality and precision, on time and within budget.

Ready to take the next step? Contact Thesun Industry today to learn how we can support your metal stamping projects, from prototype to high-volume production. Let’s work together to bring your designs to life!

